
DoubleCosineServer
Module: Essential Math Group: FFT Server classes
Does not inherit
Local Index
Members
Synopsis
#include <rw/dcosfft.h> DoubleCosineServer a;
Description
Class DoubleCosineServer performs double precision fast sine or cosine transforms of a real vector. The transform of a real, even sequence is a cosine transform. The transform of a real, odd sequence is a sine transform.
Even Sequence:
A real even vector is symmetric, that is, V(j) == V(-j) or V(j) == V(2N-j), where 2N is the total length of the vector. Of the 2N points, only the N+1 points V(j), j=0, ... , N need be given. The upper half of V can be recovered from V(j) = V(2N-j), j = N+1, ... , 2N-1. This means that of the total 2N sequence, N-1 values are repeated twice and two [V(0) and V(N)] are unique. This produces a total of 2N points, of which only N+1 are actually stored.
The inverse Fourier transform (IDFT) of a real even sequence is a cosine transform. The result is also a real even sequence. The transform is defined as follows. As above, assume that V(j), j = 0, 1, 2, ..., 2N-1 is real, and that V(j) == V(2N-j). Then:
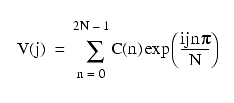
or: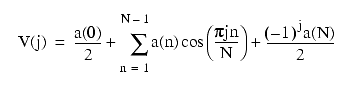
where the a(n)s are real and a(n) = 2C(n).
It also follows that the forward Fourier transform (DFT) of V(j) can be expressed as a cosine series:
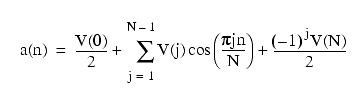
Only the real part of C(n) is actually returned by cosine().
Odd Sequence:
A real odd vector is antisymmetric, that is, V(j) == -V(-j) or V(j) == -V(2N-j). As above, the vector V should be thought of as 2N points long, but here only the points V(j), j=1, ..., N-1, a total of N-1 points, need be given. This is true because we know that V(0) and V(N) are always 0 if the sequence is odd. Consequently, of the total 2N sequence, N-1 values are repeated twice and two are always 0. This produces a total of 2N points, of which only N-1 are actually stored.
The sine transform is defined as:
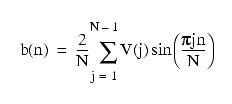
and:
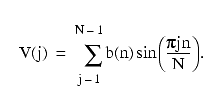
Only the imaginary part of C(n) is actually returned by sine().
Due to an algorithmic limitation, the cosine and sine transforms are limited to sequences with N even. In other words, the length() of the vector V must be odd.
Speed Note: In general, you have the choice of using a cosine transform, or expanding to the full series and using a regular complex FFT, saving only the lower half of the real part. In reality, the cosine transform performs worst relative to the regular complex FFT for short series that are a power of 2 in length (empirically, the series that are 32, 16, 8, ... points long). For this reason, you might want to consider using the complex transform. For longer series, however, or for series that are not a power of 2 in length, it is better to use the cosine server. This also lets you use optimizations later.
Public Constructors
DoubleCosineServer();
Constructs a double precision cosine server for a vector of unspecified length. This length is initialized when the server is used.
DoubleCosineServer(unsigned N);
Constructs a cosine server designed to transform a vector of length N.
DoubleCosineServer(const DoubleCosineServer&);
Copy constructor. The new server references the old server's data.
Public Member Functions
RWMathVec<double> cosine(const RWMathVec<double>& v);
Returns the cosine transform of a real vector.
RWMathVec<double> icosine(const RWMathVec<double>& v);
Returns the inverse cosine transform of a real vector.
RWMathVec<double> isine(const RWMathVec<double>& v);
Returns the inverse sine transform of a real vector.
unsigned order() const;
Returns the order of a cosine server, that is, the vector length it is currently configured to transform.
void setOrder(unsigned N);
Resets the order of a cosine server to N.
RWMathVec<double> sine(const RWMathVec<double>& v);
Returns the sine transform of a real vector.
Public Member Operator
void operator=(const DoubleCosineServer& v);
Sets self to the same order as v.
© Copyright Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Rogue Wave and SourcePro are registered trademarks of Rogue Wave Software, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Contact Rogue Wave about documentation or support issues.