This example trains a 2-layer network using 100 training patterns from one nominal and one continuous input attribute. The nominal attribute has three classifications which are encoded using binary encoding. This results in three binary network input columns. The continuous input attribute is scaled to fall in the interval [0,1].
The network training targets were generated using the relationship:
y = 10*X1 + 20*X2 + 30*X3 + 2.0*X4 , where
X1 -X3 are the three binary columns, corresponding to categories 1-3 of the nominal attribute, and X4 is the scaled continuous attribute.
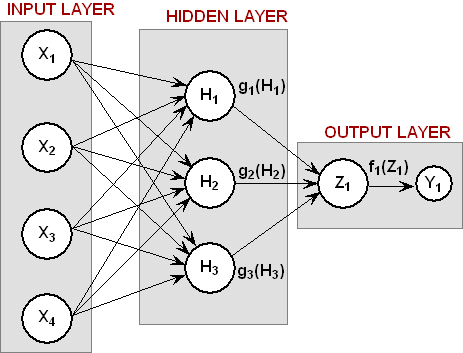
The structure of the network consists of four input nodes and two layers, with three perceptrons in the hidden layer and one in the output layer. The following figure illustrates this structure:

There are a total of 19 weights in this network. The activations functions are all linear. Since the target output is a linear function of the input attributes, linear activation functions guarantee that the network forecasts will exactly match their targets. Of course, this same result could have been obtained using linear multiple regression. Training is conducted using the quasi-newton trainer.
using System;
using Imsl.DataMining.Neural;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
//*****************************************************************************
// Two Layer Feed-Forward Network with 4 inputs: 1 nominal with 3 categories,
// encoded using binary encoding, 1 continuous input attribute, and 1 output
// target (continuous).
// There is a perfect linear relationship between the input and output
// variables:
//
// MODEL: Y = 10*X1+20*X2+30*X3+2*X4
//
// Variables X1-X3 are the binary encoded nominal variable and X4 is the
// continuous variable.
//*****************************************************************************
//[Serializable]
public class FeedForwardNetworkEx1 //: System.Runtime.Serialization.ISerializable
{
// Network Settings
private static int nObs = 100; // number of training patterns
private static int nInputs = 4; // four inputs
private static int nCategorical = 3; // three categorical attributes
private static int nOutputs = 1; // one continuous output
private static int nPerceptrons = 3; // perceptrons in hidden layer
private static IActivation hiddenLayerActivation;
private static IActivation outputLayerActivation;
private static System.String errorMsg = "";
// Error Status Messages for the Least Squares Trainer
private static System.String errorMsg0 =
"--> Least Squares Training Completed Successfully";
private static System.String errorMsg1 =
"--> Scaled step tolerance was satisfied. The current solution \n" +
"may be an approximate local solution, or the algorithm is making\n" +
"slow progress and is not near a solution, or the Step Tolerance\n" +
"is too big";
private static System.String errorMsg2 =
"--> Scaled actual and predicted reductions in the function are\n" +
"less than or equal to the relative function convergence\n" +
"tolerance RelativeTolerance";
private static System.String errorMsg3 =
"--> Iterates appear to be converging to a noncritical point.\n" +
"Incorrect gradient information, a discontinuous function,\n" +
"or stopping tolerances being too tight may be the cause.";
private static System.String errorMsg4 =
"--> Five consecutive steps with the maximum stepsize have\n" +
"been taken. Either the function is unbounded below, or has\n" +
"a finite asymptote in some direction, or the maximum stepsize\n" +
"is too small.";
private static System.String errorMsg5 =
"--> Too many iterations required";
// categoricalAtt[]: A 2D matrix of values for the categorical training
// attribute. In this example, the single categorical
// attribute has 3 categories that are encoded using
// binary encoding for input into the network.
// {1,0,0} = category 1, {0,1,0} = category 2, and
// {0,0,1} = category 3.
private static double[,] categoricalAtt =
{{1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}};
//
// contAtt[]: A matrix of values for the continuous training attribute
//
private static double[] contAtt = new double[]{4.007054658, 7.10028447,
4.740350984, 5.714553211, 6.205437459, 2.598930065, 8.65089967,
5.705787357, 2.513348184, 2.723795955, 4.1829356, 1.93280416,
0.332941608, 6.745567628, 5.593588463, 7.273544478, 3.162117939,
4.205381208, 0.16414745, 2.883418275, 0.629342241, 1.082223406,
8.180324708, 8.004894314, 7.856215418, 7.797143157, 8.350033996,
3.778254431, 6.964837082, 6.13938006, 0.48610387, 5.686627923,
8.146173848, 5.879852653, 4.587492779, 0.714028533, 7.56324211,
8.406012623, 4.225261454, 6.369220241, 4.432772218, 9.52166984,
7.935791508, 4.557155333, 7.976015058, 4.913538616, 1.473658514,
2.592338905, 1.386872932, 7.046051685, 1.432128376, 1.153580985,
5.6561491, 3.31163251, 4.648324851, 5.042514515, 0.657054195,
7.958308093, 7.557870384, 7.901990083, 5.2363088, 6.95582150,
8.362167045, 4.875903563, 1.729229471, 4.380370223, 8.527875685,
2.489198107, 3.711472959, 4.17692681, 5.844828801, 4.825754155,
5.642267843, 5.339937786, 4.440813223, 1.615143829, 7.542969339,
8.100542684, 0.98625265, 4.744819569, 8.926039258, 8.813441887,
7.749383991, 6.551841576, 8.637046998, 4.560281415, 1.386055087,
0.778869034, 3.883379045, 2.364501589, 9.648737525, 1.21754765,
3.908879368, 4.253313879, 9.31189696, 3.811953836, 5.78471629,
3.414486452, 9.345413015, 1.024053777};
//
// outs[]: A 2D matrix containing the training outputs for this network
// In this case there is an exact linear relationship between these
// outputs and the inputs: outs = 10*X1+20*X2+30*X3+2*X4, where
// X1-X3 are the categorical variables and X4=contAtt
//
private static double[] outs = new double[]{18.01410932, 24.20056894,
19.48070197, 21.42910642, 22.41087492, 15.19786013, 27.30179934,
21.41157471, 15.02669637, 15.44759191, 18.3658712, 13.86560832,
10.66588322, 23.49113526, 21.18717693, 24.54708896, 16.32423588,
18.41076242, 10.3282949, 15.76683655, 11.25868448, 12.16444681,
26.36064942, 26.00978863, 25.71243084, 25.59428631, 26.70006799,
17.55650886, 23.92967416, 22.27876012, 10.97220774, 21.37325585,
26.2923477, 21.75970531, 19.17498556, 21.42805707, 35.12648422,
36.81202525, 28.45052291, 32.73844048, 28.86554444, 39.04333968,
35.87158302, 29.11431067, 35.95203012, 29.82707723, 22.94731703,
25.18467781, 22.77374586, 34.09210337, 22.86425675, 22.30716197,
31.3122982, 26.62326502, 29.2966497, 30.08502903, 21.31410839,
35.91661619, 35.11574077, 35.80398017, 30.4726176, 33.91164302,
36.72433409, 29.75180713, 23.45845894, 38.76074045, 47.05575137,
34.97839621, 37.42294592, 38.35385362, 41.6896576, 39.65150831,
41.28453569, 40.67987557, 38.88162645, 33.23028766, 45.08593868,
46.20108537, 31.9725053, 39.48963914, 47.85207852, 47.62688377,
45.49876798, 43.10368315, 47.274094, 39.1205628, 32.77211017,
31.55773807, 37.76675809, 34.72900318, 49.29747505, 32.4350953,
37.81775874, 38.50662776, 48.62379392, 37.62390767, 41.56943258,
36.8289729, 48.69082603, 32.04810755};
// **********************************************************************
// MAIN
// **********************************************************************
public static void Main(System.String[] args)
{
double[] weight; // network weights
double[] gradient; // network gradient after training
double[,] xData; // Input Attributes for Trainer
double[,] yData; // Output Attributes for Trainer
int i, j; // array indicies
int nWeights = 0; // Number of weights obtained from network
System.String networkFileName = "FeedForwardNetworkEx1.ser";
System.String trainerFileName = "FeedForwardTrainerEx1.ser";
System.String xDataFileName = "FeedForwardxDataEx1.ser";
System.String yDataFileName = "FeedForwardyDataEx1.ser";
// **********************************************************************
// PREPROCESS TRAINING PATTERNS
// **********************************************************************
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"--> Starting Preprocessing of Training Patterns");
xData = new double[nObs,nInputs];
// for (int i2 = 0; i2 < nObs; i2++)
// {
// xData[i2] = new double[nInputs];
// }
yData = new double[nObs,nOutputs];
// for (int i3 = 0; i3 < nObs; i3++)
// {
// yData[i3] = new double[nOutputs];
// }
for (i = 0; i < nObs; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < nCategorical; j++)
{
xData[i,j] = categoricalAtt[i,j];
}
xData[i,nCategorical] = contAtt[i] / 10.0; // Scale continuous input
yData[i,0] = outs[i]; // outputs are unscaled
}
// **********************************************************************
// CREATE FEEDFORWARD NETWORK
// **********************************************************************
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Creating Feed Forward Network Object");
FeedForwardNetwork network = new FeedForwardNetwork();
// setup input layer with number of inputs = nInputs = 4
network.InputLayer.CreateInputs(nInputs);
// create a hidden layer with nPerceptrons=3 perceptrons
network.CreateHiddenLayer().CreatePerceptrons(nPerceptrons);
// create output layer with nOutputs=1 output perceptron
network.OutputLayer.CreatePerceptrons(nOutputs);
// link all inputs and perceptrons to all perceptrons in the next layer
network.LinkAll();
// Get Network Perceptrons for Setting Their Activation Functions
Perceptron[] perceptrons = network.Perceptrons;
// Set all perceptrons to linear activation
for (i = 0; i < perceptrons.Length - 1; i++)
{
perceptrons[i].Activation = hiddenLayerActivation;
}
perceptrons[perceptrons.Length - 1].Activation = outputLayerActivation;
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"--> Feed Forward Network Created with 2 Layers");
// **********************************************************************
// TRAIN NETWORK USING QUASI-NEWTON TRAINER
// **********************************************************************
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"--> Training Network using Quasi-Newton Trainer");
// Create Trainer
QuasiNewtonTrainer trainer = new QuasiNewtonTrainer();
// Set Training Parameters
trainer.MaximumTrainingIterations = 1000;
// Train Network
trainer.Train(network, xData, yData);
// Check Training Error Status
switch (trainer.ErrorStatus)
{
case 0: errorMsg = errorMsg0;
break;
case 1: errorMsg = errorMsg1;
break;
case 2: errorMsg = errorMsg2;
break;
case 3: errorMsg = errorMsg3;
break;
case 4: errorMsg = errorMsg4;
break;
case 5: errorMsg = errorMsg5;
break;
default: errorMsg = errorMsg0;
break;
}
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(errorMsg);
// **********************************************************************
// DISPLAY TRAINING STATISTICS
// **********************************************************************
double[] stats = network.ComputeStatistics(xData, yData);
// Display Network Errors
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"***********************************************");
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> SSE: " +
(float) stats[0]);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> RMS: " +
(float) stats[1]);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Laplacian Error: " +
(float) stats[2]);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Scaled Laplacian Error: " +
(float) stats[3]);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Largest Absolute Residual: " +
(float) stats[4]);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"***********************************************");
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("");
// **********************************************************************
// OBTAIN AND DISPLAY NETWORK WEIGHTS AND GRADIENTS
// **********************************************************************
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Getting Network Weights and Gradients");
// Get weights
weight = network.Weights;
// Get number of weights = number of gradients
nWeights = network.NumberOfWeights;
// Obtain Gradient Vector
gradient = trainer.ErrorGradient;
// Print Network Weights and Gradients
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(" ");
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Network Weights and Gradients:");
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"***********************************************");
for (i = 0; i < nWeights; i++)
{
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("w[" + i + "]=" + (float) weight[i] +
" g[" + i + "]=" + (float) gradient[i]);
}
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(
"***********************************************");
// **********************************************************************
// SAVE THE TRAINED NETWORK BY SAVING THE SERIALIZED NETWORK OBJECT
// **********************************************************************
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("\n--> Saving Trained Network into " +
networkFileName);
write(network, networkFileName);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Saving xData into " + xDataFileName);
write(xData, xDataFileName);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Saving yData into " + yDataFileName);
write(yData, yDataFileName);
System.Console.Out.WriteLine("--> Saving Network Trainer into " +
trainerFileName);
write(trainer, trainerFileName);
}
// **************************************************************************
// WRITE SERIALIZED NETWORK TO A FILE
// **************************************************************************
static public void write(System.Object obj, System.String filename)
{
System.IO.FileStream fos = new System.IO.FileStream(filename,
System.IO.FileMode.Create);
IFormatter oos = new BinaryFormatter();
oos.Serialize(fos, obj);
fos.Close();
}
static FeedForwardNetworkEx1()
{
hiddenLayerActivation = Imsl.DataMining.Neural.Activation.Linear;
outputLayerActivation = Imsl.DataMining.Neural.Activation.Linear;
}
}
--> Starting Preprocessing of Training Patterns --> Creating Feed Forward Network Object --> Feed Forward Network Created with 2 Layers --> Training Network using Quasi-Newton Trainer --> Least Squares Training Completed Successfully *********************************************** --> SSE: 1.013444E-15 --> RMS: 2.007463E-19 --> Laplacian Error: 3.005804E-07 --> Scaled Laplacian Error: 3.535235E-10 --> Largest Absolute Residual: 2.784275E-08 *********************************************** --> Getting Network Weights and Gradients --> Network Weights and Gradients: *********************************************** w[0]=-1.491785 g[0]=-2.611079E-08 w[1]=-1.491785 g[1]=-2.611079E-08 w[2]=-1.491785 g[2]=-2.611079E-08 w[3]=1.616918 g[3]=6.182035E-08 w[4]=1.616918 g[4]=6.182035E-08 w[5]=1.616918 g[5]=6.182035E-08 w[6]=4.725622 g[6]=-5.273856E-08 w[7]=4.725622 g[7]=-5.273856E-08 w[8]=4.725622 g[8]=-5.273856E-08 w[9]=6.217407 g[9]=-8.733E-10 w[10]=6.217407 g[10]=-8.733E-10 w[11]=6.217407 g[11]=-8.733E-10 w[12]=1.072258 g[12]=-1.690978E-07 w[13]=1.072258 g[13]=-1.690978E-07 w[14]=1.072258 g[14]=-1.690978E-07 w[15]=3.850755 g[15]=-1.7029E-08 w[16]=3.850755 g[16]=-1.7029E-08 w[17]=3.850755 g[17]=-1.7029E-08 w[18]=2.411725 g[18]=-1.588144E-08 *********************************************** --> Saving Trained Network into FeedForwardNetworkEx1.ser --> Saving xData into FeedForwardxDataEx1.ser --> Saving yData into FeedForwardyDataEx1.ser --> Saving Network Trainer into FeedForwardTrainerEx1.serLink to C# source.