
SourcePro C++ 12.0
SourcePro® C++ API Reference Guide
SourcePro C++
Documentation Home
 SourcePro C++ 12.0 |
SourcePro® C++ API Reference Guide |
SourcePro C++ Documentation Home |
A templatized arbitrary dimension array class. More...
#include <rw/math/mtharray.h>
Inherits RWArrayView.
Public Types | |
| typedef RWMathArrayIterator< T > | iterator |
| typedef RWMathArrayConstIterator< T > | const_iterator |
| typedef rw_numeric_traits< T > ::promote_type | promote_type |
| typedef rw_numeric_traits< T > ::norm_type | norm_type |
| typedef rw_numeric_traits< T > ::mathFunType | mathFunType |
| typedef rw_numeric_traits< T > ::mathFunType2 | mathFunType2 |
Public Member Functions | |
| iterator | begin () |
| iterator | end () |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| RWMathArray () | |
| RWMathArray (const RWIntVec &n, RWUninitialized, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) | |
| RWMathArray (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, RWUninitialized) | |
| RWMathArray (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p, RWUninitialized) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWIntVec &vec, RWTRand< RWRandGenerator > &r, Storage s=COLUMN_MAJOR) | |
| RWMathArray (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, RWTRand< RWRandGenerator > &r) | |
| RWMathArray (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p, RWTRand< RWRandGenerator > &r) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWIntVec &vec, T val) | |
| RWMathArray (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, T val) | |
| RWMathArray (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p, T val) | |
| RWMathArray (const char *s) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWMathArray< T > &a) | |
| RWMathArray (const T *dat, const RWIntVec &n) | |
| RWMathArray (const T *dat, size_t m, size_t n, size_t o) | |
| RWMathArray (const T *dat, size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWMathVec< T > &vec, const RWIntVec &n) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWMathVec< T > &vec, size_t m, size_t n, size_t o) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWMathVec< T > &vec, size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWMathVec< T > &) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWGenMat< T > &) | |
| RWMathArray (const RWMathArray< double > &re, const RWMathArray< double > &im) | |
| RWMathArray< T > | apply (mathFunType f) const |
| RWMathArray< norm_type > | apply2 (mathFunType2 f) const |
| size_t | binaryStoreSize () const |
| RWMathArray< T > | copy () const |
| T * | data () |
| const T * | data () const |
| RWMathArray< T > | deepCopy () const |
| void | deepenShallowCopy () |
| size_t | dimension () const |
| RWIntVec | length () const |
| int | length (int i) const |
| RWMathArray< T > & | reference (const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| void | resize (const RWIntVec &v, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) |
| void | resize (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) |
| void | resize (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) |
| void | reshape (const RWIntVec &v, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) |
| void | reshape (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) |
| void | reshape (size_t m, size_t n, size_t o, size_t p, Storage storage=COLUMN_MAJOR) |
| void | restoreFrom (RWFile &) |
| void | restoreFrom (RWvistream &) |
| void | saveOn (RWFile &) const |
| void | saveOn (RWvostream &) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | slice (const RWIntVec &start, const RWIntVec &lgt, const RWGenMat< int > &strider) const |
| T & | operator[] (const RWIntVec &i) |
| T | operator[] (const RWIntVec &i) const |
| T & | operator() (const RWIntVec &i) |
| T | operator() (const RWIntVec &i) const |
| T & | operator() (int i, int j, int k) |
| T | operator() (int i, int j, int k) const |
| T & | operator() (int i, int j, int k, int l) |
| T | operator() (int i, int j, int k, int l) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, int k) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, int k) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, int k) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, int k) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, int j, const RWSlice &k) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, int j, const RWSlice &k) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, int k, int l) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, int k, int l) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, int k, int l) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, int k, int l) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, int j, const RWSlice &k, int l) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, int j, const RWSlice &k, int l) const |
| RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, int j, int k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWMathVec< T > | operator() (int i, int j, int k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, const RWSlice &k) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, const RWSlice &k) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, int k) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, int k) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, int j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, int j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, int k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, int k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, int l) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, int l) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, int k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, int k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, const RWSlice &k, int l) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, const RWSlice &k, int l) const |
| RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, int k, int l) |
| const RWGenMat< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, int k, int l) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k) |
| const RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWMathArray< T > | operator() (int i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, int j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, int k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, int k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, int l) |
| const RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, int l) const |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) |
| const RWMathArray< T > | operator() (const RWSlice &i, const RWSlice &j, const RWSlice &k, const RWSlice &l) const |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator= (const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator= (const T &s) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator+= (const T &s) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator-= (const T &s) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator*= (const T &s) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator/= (const T &s) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator+= (const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator-= (const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator*= (const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator/= (const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator++ () |
| RWMathArray< T > & | operator-- () |
| void | operator++ (int) |
| void | operator-- (int) |
| bool | operator== (const RWMathArray< T > &v) const |
| bool | operator!= (const RWMathArray< T > &v) const |
| operator RWMathArray< promote_type > () | |
Friends | |
| RWMathArray< double > | real (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &) |
| RWMathArray< double > | imag (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &) |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator- (const RWMathArray< T > &u) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator+ (const RWMathArray< T > &u) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator+ (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator- (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator* (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator/ (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator+ (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const T &s) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator- (const T &s, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator* (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const T &s) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator/ (const T &s, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator/ (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const T &s) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator* (const T &s, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator+ (const T &s, const RWMathArray< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | operator- (const RWMathArray< T > &u, const T &s) |
| RWMathArray< double > | abs (const RWMathArray< double > &) |
| RWMathArray< float > | abs (const RWMathArray< float > &) |
| RWMathArray< int > | abs (const RWMathArray< int > &) |
| RWMathArray< double > | abs (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &) |
| RWMathArray< SChar > | abs (const RWMathArray< SChar > &) |
| RWMathArray< double > | norm (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &) |
| double | maxNorm (const RWMathArray< double > &v) |
| float | maxNorm (const RWMathArray< float > &v) |
| double | maxNorm (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &v) |
| double | frobNorm (const RWMathArray< double > &v) |
| float | frobNorm (const RWMathArray< float > &v) |
| double | frobNorm (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | toScalar (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathVec< T > | toVec (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWGenMat< T > | toGenMat (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| RWMathArray< float > | toFloat (const RWMathArray< double > &v) |
| RWMathArray< int > | toInt (const RWMathArray< double > &v) |
| RWMathArray< int > | toInt (const RWMathArray< float > &v) |
| RWMathArray< SChar > | toChar (const RWMathArray< int > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWIntVec | maxIndex (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | maxValue (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWIntVec | minIndex (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | minValue (const RWMathArray< T > &) |
| RWMathArray< double > | arg (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &v) |
| RWMathArray< DComplex > | conj (const RWMathArray< DComplex > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | cos (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | cosh (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | exp (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | mean (const RWMathArray< T > &V) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | pow (const RWMathArray< T > &x, const RWMathArray< T > &y) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | pow (const RWMathArray< T > &x, T y) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | pow (T x, const RWMathArray< T > &y) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | sin (const RWMathArray< T > &V) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | sinh (const RWMathArray< T > &V) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | sqrt (const RWMathArray< T > &V) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | acos (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | asin (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | atan (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | atan2 (const RWMathArray< T > &x, const RWMathArray< T > &y) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | ceil (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | floor (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | log (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | log10 (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | tan (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| RWMathArray< T > | tanh (const RWMathArray< T > &x) |
Class RWMathArray<T> is a templatized arbitrary dimension array class.
#include <rw/math/mtharray.h> RWMathArray<T> array;
#include <rw/math/mtharray.h> int main() { RWMathArray<DComplex> A(3,3,3, DComplex(3,0)); RWMathArray<DComplex> B(5,5,5,5,reUninitialized); // Set a plane of data to 5 + 2i A(RWAll,0,RWAll) = DComplex(5,2); }
| typedef RWMathArrayConstIterator<T> RWMathArray< T >::const_iterator |
Typedef for a random access const iterator.
| typedef RWMathArrayIterator<T> RWMathArray< T >::iterator |
Typedef for a random access iterator.
| typedef rw_numeric_traits<T>::mathFunType RWMathArray< T >::mathFunType |
Typedef for the function pointer used in the method apply(). For more information, see rw_numeric_traits<T>::mathFunType.
| typedef rw_numeric_traits<T>::mathFunType2 RWMathArray< T >::mathFunType2 |
Typedef for the function pointer used in the method apply2(). For more information, see rw_numeric_traits<T>::mathFunType2.
| typedef rw_numeric_traits<T>::norm_type RWMathArray< T >::norm_type |
Typedef for the usual return type of numerical norm-like functions. For more information, see rw_numeric_traits<T>::norm_type.
| typedef rw_numeric_traits<T>::promote_type RWMathArray< T >::promote_type |
Typedef for the promotion type. For more information, see rw_numeric_traits<T>::promote_type.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | ) |
Constructs a 0-dimensional array, useful for declaring vectors of arrays. Like any other array, this array can subsequently be reshaped or resized (see member functions reshape() and resize()). Note that since this is a 0-dimensional (not 0 length) array, and since by definition a 0-dimensional array is a scalar, the array has one element of data.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWIntVec & | n, | |
| RWUninitialized | , | |||
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Constructs an uninitialized array with a specified size. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions. The RWUninitialized type is an enumeration type with only one value, rwUninitialized. The rwUninitialized argument is used to distinguish the last dimension size from an initial value.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| RWUninitialized | ||||
| ) |
Constructs an uninitialized array with a specified size. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions. The RWUninitialized type is an enumeration type with only one value, rwUninitialized. The rwUninitialized argument is used to distinguish the last dimension size from an initial value.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p, | |||
| RWUninitialized | ||||
| ) |
Constructs an uninitialized array with a specified size. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions. The RWUninitialized type is an enumeration type with only one value, rwUninitialized. The rwUninitialized argument is used to distinguish the last dimension size from an initial value.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWIntVec & | vec, | |
| RWTRand< RWRandGenerator > & | r, | |||
| Storage | s = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size initialized with random numbers generated by r. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| RWTRand< RWRandGenerator > & | r | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size initialized with random numbers generated by r. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p, | |||
| RWTRand< RWRandGenerator > & | r | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size initialized with random numbers generated by r. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWIntVec & | vec, | |
| T | val | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size. Each element in the array is initialized to val. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| T | val | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size. Each element in the array is initialized to val. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p, | |||
| T | val | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size. Each element in the array is initialized to val. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const char * | s | ) |
Constructs an array from the null terminated character string s. The format of the character string is the same as that expected by the global operator operator>> described in this entry.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | a | ) | [inline] |
Copy constructor. The new array and the old array both view the same data.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const T * | dat, | |
| const RWIntVec & | n | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size using the data in the vector dat as initial data. A copy of dat is made. The vector dat must have at least as many elements as the array. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const T * | dat, | |
| size_t | m, | |||
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size using the data in the vector dat as initial data. A copy of dat is made. The vector dat must have at least as many elements as the array. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const T * | dat, | |
| size_t | m, | |||
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array with a specified size using the data in the vector dat as initial data. A copy of dat is made. The vector dat must have at least as many elements as the array. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWMathVec< T > & | vec, | |
| const RWIntVec & | n | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array using the data in the vector vec. The array is a new view of the same data as vec, so no copy of the data is made. The vector vec must have the same number of elements as the array. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWMathVec< T > & | vec, | |
| size_t | m, | |||
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array using the data in the vector vec. The array is a new view of the same data as vec, so no copy of the data is made. The vector vec must have the same number of elements as the array. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWMathVec< T > & | vec, | |
| size_t | m, | |||
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p | |||
| ) |
Constructs an array using the data in the vector vec. The array is a new view of the same data as vec, so no copy of the data is made. The vector vec must have the same number of elements as the array. The constructor taking an integer vector is useful for constructing arrays with more than four dimensions.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWMathVec< T > & | ) |
Constructs a 1-dimensional or 2-dimensional array from a vector or matrix. The resulting array is an alternate view of the same data. This constructor is most often used implicitly by the compiler to pass vectors or matrices to subroutines written to operate on arrays of arbitrary dimension. This allows you to write one subroutine suitable for vectors, matrices, or arrays.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWGenMat< T > & | ) |
Constructs a 1-dimensional or 2-dimensional array from a vector or matrix. The resulting array is an alternate view of the same data. This constructor is most often used implicitly by the compiler to pass vectors or matrices to subroutines written to operate on arrays of arbitrary dimension. This allows you to write one subroutine suitable for vectors, matrices, or arrays.
| RWMathArray< T >::RWMathArray | ( | const RWMathArray< double > & | re, | |
| const RWMathArray< double > & | im | |||
| ) |
Constructs a complex array from the double precision arrays re and im, with the real part of the array equal to re and the imaginary part equal to im. A new copy of the data is made.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::apply | ( | mathFunType | f | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the result of applying the passed function to every element in the array. A function of type RWMathArray<T>::mathFunType takes and returns a T; a function of type RWMathArray<T>::mathFunType2 takes a T and returns an RWMathArray<T>::norm_type. See class rw_numeric_traits for a description of RWMathArray<T>::norm_type.
| RWMathArray<norm_type> RWMathArray< T >::apply2 | ( | mathFunType2 | f | ) | const |
Returns the result of applying the passed function to every element in the array. A function of type RWMathArray<T>::mathFunType takes and returns a T; a function of type RWMathArray<T>::mathFunType2 takes a T and returns an RWMathArray<T>::norm_type. See class rw_numeric_traits for a description of RWMathArray<T>::norm_type.
| const_iterator RWMathArray< T >::begin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns an iterator pointing to the first element of self.
| iterator RWMathArray< T >::begin | ( | ) | [inline] |
Returns an iterator pointing to the first element of self.
| size_t RWMathArray< T >::binaryStoreSize | ( | ) | const |
Returns the number of bytes required to store the array to an RWFile using member function saveOn(RWFile&).
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::copy | ( | ) | const |
Returns a copy with distinct instance variables. The function copy() is a synonym for deepCopy().
| const T* RWMathArray< T >::data | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Returns a pointer to the start of an array's data. Should be used with care, as this accesses the array's data directly.
| T* RWMathArray< T >::data | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Returns a pointer to the start of an array's data. Should be used with care, as this accesses the array's data directly.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::deepCopy | ( | ) | const |
Returns a copy with distinct instance variables. The function copy() is a synonym for deepCopy().
| void RWMathArray< T >::deepenShallowCopy | ( | ) |
When invoked for an array, guarantees that there is only one reference to that object and that its data are in contiguous memory.
| size_t RWMathArray< T >::dimension | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the number of dimensions of the array.
| const_iterator RWMathArray< T >::end | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns an iterator pointing to one element past the last element of self.
| iterator RWMathArray< T >::end | ( | ) | [inline] |
Returns an iterator pointing to one element past the last element of self.
| int RWMathArray< T >::length | ( | int | i | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the size of the indicated dimension.
| RWIntVec RWMathArray< T >::length | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the number of entries in a dimension of the array, returning all the dimension lengths at once.
| RWMathArray< T >::operator RWMathArray< promote_type > | ( | ) | [inline] |
Implicit conversion operator to rw_numeric_traits<T>::promote_type.
| bool RWMathArray< T >::operator!= | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) | const |
Returns true if self and the argument are equivalent (or not equivalent). To be equivalent, they must have the same number of rows as well as columns, and each element in self must equal the corresponding element in the argument.
| const RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathArray that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathArray being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWGenMat<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWGenMat that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWGenMat being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| const RWSlice & | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| const RWSlice & | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| const RWSlice & | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| const RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) | const |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| RWMathVec<T> RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWSlice & | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a non-const RWMathVec that contains the elements at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array. The RWMathVec being returned is a new view of the same data as the array being subscripted.
| T RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | const [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns the element at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array.
| T & RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k, | |||
| int | l | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a reference to the element at (i th, j th, k th, l th) position of the array.
| T RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) | const [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns the element at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array.
| T & RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| int | k | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a reference to the element at (i th, j th, k th) position of the array.
| T RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWIntVec & | i | ) | const [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns the element indexed by i.
| T & RWMathArray< T >::operator() | ( | const RWIntVec & | i | ) | [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with optional bounds checking. Bounds checking is enabled by defining the preprocessor macro RWBOUNDS_CHECK before including the header file. Returns a reference to the element indexed by i.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator*= | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) |
Assignment by multiplication operator with conventional meaning. The expression 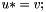 implies
implies 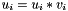 The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator*= | ( | const T & | s | ) |
Assignment by multiplication operator with conventional meaning. The expression 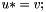 implies
implies 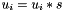
| void RWMathArray< T >::operator++ | ( | int | ) | [inline] |
Increments or decrements each element of self. The functions taking an integer parameter are invoked if the operator is used as a postfix operator.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator++ | ( | ) |
Increments or decrements each element of self. The functions taking an integer parameter are invoked if the operator is used as a postfix operator.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator+= | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) |
Assignment by addition operator with conventional meaning. The expression 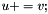 implies
implies 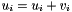 The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator+= | ( | const T & | s | ) |
Assignment by addition operator with conventional meaning. The expression 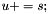 implies
implies 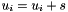
| void RWMathArray< T >::operator-- | ( | int | ) | [inline] |
Increments or decrements each element of self. The functions taking an integer parameter are invoked if the operator is used as a postfix operator.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator-- | ( | ) |
Increments or decrements each element of self. The functions taking an integer parameter are invoked if the operator is used as a postfix operator.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator-= | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) |
Assignment by subtraction operator with conventional meaning. The expression
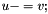 implies
implies 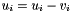 The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator-= | ( | const T & | s | ) | [inline] |
Assignment by subtraction operator with conventional meaning. The expression 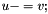 implies
implies 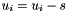
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator/= | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) |
Assignment by division operator with conventional meaning. The expression 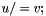 implies
implies 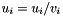 The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator/= | ( | const T & | s | ) |
Assignment by division operator with conventional meaning. The expression 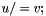 implies
implies 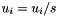
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator= | ( | const T & | s | ) |
Assignment operator with conventional meaning. The expression 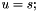 implies
implies 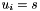 .
.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::operator= | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) |
Assignment operator with conventional meaning. The expression 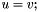 implies
implies 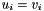 The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
The RWMathArray objects must conform, that is, have the same dimensions.
| bool RWMathArray< T >::operator== | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) | const |
Returns true if self and the argument are equivalent (or not equivalent). To be equivalent, they must have the same number of rows as well as columns, and each element in self must equal the corresponding element in the argument.
| T RWMathArray< T >::operator[] | ( | const RWIntVec & | i | ) | const [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with bounds checking. Returns the element indexed by i.
| T & RWMathArray< T >::operator[] | ( | const RWIntVec & | i | ) | [inline] |
Subscripting operator for the array, with bounds checking. Returns a reference to the element indexed by i.
| RWMathArray<T>& RWMathArray< T >::reference | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | v | ) |
Makes self a view of data in v. The view currently associated with the array is lost.
| void RWMathArray< T >::reshape | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p, | |||
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Changes the size of the array. After reshaping, the contents of the array are undefined; that is, they can be and probably will be garbage.
| void RWMathArray< T >::reshape | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Changes the size of the array. After reshaping, the contents of the array are undefined; that is, they can be and probably will be garbage.
| void RWMathArray< T >::reshape | ( | const RWIntVec & | v, | |
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Changes the size of the array. After reshaping, the contents of the array are undefined; that is, they can be and probably will be garbage.
| void RWMathArray< T >::resize | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| size_t | p, | |||
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Changes the size of the array, adding 0s or truncating as necessary.
| void RWMathArray< T >::resize | ( | size_t | m, | |
| size_t | n, | |||
| size_t | o, | |||
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Changes the size of the array, adding 0s or truncating as necessary.
| void RWMathArray< T >::resize | ( | const RWIntVec & | v, | |
| Storage | storage = COLUMN_MAJOR | |||
| ) |
Changes the size of the array, adding 0s or truncating as necessary.
| void RWMathArray< T >::restoreFrom | ( | RWvistream & | ) |
Restores self from a virtual stream. To use this function with a user-defined type, the corresponding operator>> must be defined:
RWvistream& operator>>(RWvistream& T&);
| void RWMathArray< T >::restoreFrom | ( | RWFile & | ) |
Restores self from a RWFile. To use this function with a user-defined type, the corresponding operator>> must be defined:
RWFile& operator>>(RWFile&, T&);
| void RWMathArray< T >::saveOn | ( | RWvostream & | ) | const |
Stores self to a RWvostream. To use these functions with a user-defined type, the corresponding operator<< must be defined:
RWvostream& operator<<(RWvostream& T&);
| void RWMathArray< T >::saveOn | ( | RWFile & | ) | const |
Stores self in a binary format to an RWFile. To use these functions with a user-defined type, the corresponding operator<< must be defined:
RWFile& operator<<(RWFile&, T&);
| RWMathArray<T> RWMathArray< T >::slice | ( | const RWIntVec & | start, | |
| const RWIntVec & | lgt, | |||
| const RWGenMat< int > & | strider | |||
| ) | const |
Returns an array that views a slice of the array. The slice begins at element start and is of size lgt. The increment between successive elements in the slice's jth dimension is given by the jth column of the matrix strider. For 3-dimensional and 4-dimensional arrays, most useful slices can be more simply constructed using subscripting.
| RWMathArray< SChar > abs | ( | const RWMathArray< SChar > & | ) | [related] |
Returns the absolute values of each element.
See the example in abs(const RWMathArray<double>&).
| RWMathArray< double > abs | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | ) | [related] |
Returns the absolute values of each element.
See the example in abs(const RWMathArray<double>&).
double. Therefore, if abs() is invoked for class RWMathArray<DComplex> , a vector of class RWMathArray<double> is returned. | RWMathArray< int > abs | ( | const RWMathArray< int > & | ) | [related] |
Returns the absolute values of each element.
See the example in abs(const RWMathArray<double>&).
| RWMathArray< float > abs | ( | const RWMathArray< float > & | ) | [related] |
Returns the absolute values of each element.
See the example in abs(const RWMathArray<double>&).
| RWMathArray< double > abs | ( | const RWMathArray< double > & | ) | [related] |
Returns the absolute values of each element.
#include <rw/math/mtharray.h> #include <iostream> const double adata[] = {1.2,2.4,-1.2,0.8,-4.5}; int main() { RWMathArray<double> a(adata,5, 1, 1); RWMathArray<double> b = abs(a); std::cout << b; return 0; }
Program Output:
5x1x1 [ 1.2 2.4 1.2 0.8 4.5 ]
| RWMathArray< T > acos | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Returns arc cosines y such that 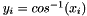 . The yi(in radians) are in the range
. The yi(in radians) are in the range 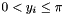 , for elements xi with absolute values
, for elements xi with absolute values 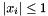 .
.
| RWMathArray< double > arg | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | v | ) | [related] |
| RWMathArray< T > asin | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns arc sines y such that 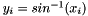 . The yi(in radians) are in the range
. The yi(in radians) are in the range 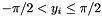 , for elements xi with absolute values
, for elements xi with absolute values 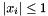 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > atan | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x and returns y of arc tangents (in radians), such that 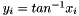 , where -
, where -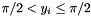 .
.
At least one of the arguments xi or yi must be nonzero.
| RWMathArray< T > atan2 | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | y | |||
| ) | [related] |
Takes two arguments and returns quadrant correct arc tangents z (in radians), such that 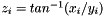 . For each element i, the expression
. For each element i, the expression 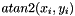 is mathematically equivalent to:
is mathematically equivalent to:
![\[ tan^{-1}\left(\frac{x_i}{y_i}\right) \]](form_136.png)
At least one of the arguments xi or yi must be nonzero.
| RWMathArray< T > ceil | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns y such that yi corresponds to the next integer greater than or equal to xi. For example, if x = [ -1.3, 4.3, 7.9] then y = [ -1, 5, 8].
| RWMathArray< DComplex > conj | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | v | ) | [related] |
Takes complex x as an argument and returns the complex conjugates x*. For example, if xi = (2.3, 1.4), then xi* = (2.3, -1.4).
| RWMathArray< T > cos | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns y such that 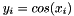 . The xi are in radians. For complex arguments, the complex cosine is returned.
. The xi are in radians. For complex arguments, the complex cosine is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > cosh | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns hyperbolic cosines y such that 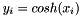 . For complex arguments, the complex hyperbolic cosine is returned.
. For complex arguments, the complex hyperbolic cosine is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > exp | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes an argument x and returns y such that:
![\[ y_i = e^{x_i} \]](form_119.png)
If class T is complex, the complex exponential is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > floor | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns y such that yi corresponds to the largest integer less than or equal to xi. For example, if x = [ 1.3, 4.4, -3.2], then y = [ 1, 4, -4].
| double frobNorm | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | v | ) | [related] |
Computes the Frobenius norm, which is the square root of the sum of squares of its entries. For a vector, the formula is:
![\[ \left \| A \right \|_{\text{Frob}} = \sqrt{\sum_{i_{0}=0}^{M_{0}-1} \sum_{i_{n-1}=0}^{M_{n-1}-1} \left | \text{a}_{i_{o}...i_{n-1}} \right |^2} \]](form_254.png)
| float frobNorm | ( | const RWMathArray< float > & | v | ) | [related] |
Computes the Frobenius norm, which is the square root of the sum of squares of its entries. For a vector, the formula is:
![\[ \left \| A \right \|_{\text{Frob}} = \sqrt{\sum_{i_{0}=0}^{M_{0}-1} \sum_{i_{n-1}=0}^{M_{n-1}-1} \left | \text{a}_{i_{o}...i_{n-1}} \right |^2} \]](form_254.png)
| double frobNorm | ( | const RWMathArray< double > & | v | ) | [related] |
Computes the Frobenius norm, which is the square root of the sum of squares of its entries. For a vector, the formula is:
![\[ \left \| A \right \|_{\text{Frob}} = \sqrt{\sum_{i_{0}=0}^{M_{0}-1} \sum_{i_{n-1}=0}^{M_{n-1}-1} \left | \text{a}_{i_{o}...i_{n-1}} \right |^2} \]](form_254.png)
| RWMathArray< double > imag | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | ) | [friend] |
Takes complex x as an argument and returns y containing the imaginary parts 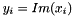 . With most versions of complex, the results can be used as an l-value:
. With most versions of complex, the results can be used as an l-value:
RWMathArray<DComplex> v(3,3,3, DComplex(3,0)); // (0, 0), (0, 0), ... imag(v) = 1.0; // (0, 1), (0, 1), ...
| RWMathArray< T > log | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns natural logarithms y such that 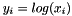 . The arguments x i must not be 0. For complex arguments, the principal value of the complex natural logarithm is returned.
. The arguments x i must not be 0. For complex arguments, the principal value of the complex natural logarithm is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > log10 | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
Takes x as an argument and returns base 10 logarithms y such that 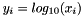 . The arguments x i must not be 0.
. The arguments x i must not be 0.
| RWIntVec maxIndex | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Return the index of the maximum element of the vector. If instead you want the maximum value use function maxValue().
| double maxNorm | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | v | ) | [related] |
Returns the value of the element with largest absolute value. Note that this is not a norm in the mathematical sense of the word.
| float maxNorm | ( | const RWMathArray< float > & | v | ) | [related] |
Returns the value of the element with largest absolute value. Note that this is not a norm in the mathematical sense of the word.
| double maxNorm | ( | const RWMathArray< double > & | v | ) | [related] |
Returns the value of the element with largest absolute value. Note that this is not a norm in the mathematical sense of the word.
| T maxValue | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Return the maximum value.
| T mean | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | V | ) | [related] |
Takes a RWMathArray an argument and returns <x>, the mean value, where:
![\[ \langle x \rangle = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}x_i \]](form_120.png)
For example, if x = [1, 4, 3, 4], then <x> = 3.
| RWIntVec minIndex | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Return the index of the minimum element of the vector. If instead you want the minimum value use function minValue().
| T minValue | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Return the minimum value.
| RWMathArray< double > norm | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | ) | [related] |
Takes complex x as an argument and returns real y containing the norm:
![$ y_{i} = [Re(x_{i})]^{2} + [Im(x_{i})]^{2} $](form_148.png) .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator* | ( | const T & | s, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Multiplication operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices v, w, and scaler s, the expression 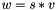 implies
implies  .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator* | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const T & | s | |||
| ) | [related] |
Multiplication operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, w, and scaler s, the expression 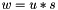 implies
implies 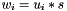 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator* | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Multiplication operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, v, and w, the expression 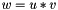 implies
implies 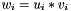 . Therefore, operator*() implies an element-by-element multiply, not the inner product. The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value
. Therefore, operator*() implies an element-by-element multiply, not the inner product. The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value RWMATH_NMATCH occurs.
| RWMathArray< T > operator+ | ( | const T & | s, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Addition operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices v, w, and scaler s, the expression 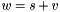 implies
implies 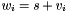 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator+ | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const T & | s | |||
| ) | [related] |
Addition operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, w, and scaler s, the expression 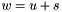 implies
implies 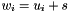 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator+ | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Addition operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, v, and w, the expression 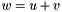 implies
implies 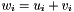 . The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value
. The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value RWMATH_NMATCH occurs.
| RWMathArray< T > operator+ | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u | ) | [related] |
Unary plus operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrix u, and w, the expression 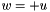 implies
implies 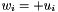 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator- | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const T & | s | |||
| ) | [related] |
Subtraction operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, w, and scaler s, the expression 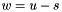 implies
implies 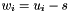 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator- | ( | const T & | s, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Subtraction operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices v, w, and scaler s, the expression 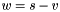 implies
implies 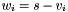 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator- | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Subtraction operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, v, and w, the expression 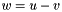 implies
implies 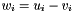 . The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value
. The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value RWMATH_NMATCH occurs.
| RWMathArray< T > operator- | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u | ) | [related] |
Unary minus operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrix u, and w, the expression 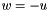 implies
implies 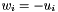 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator/ | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const T & | s | |||
| ) | [related] |
Division operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, w, and scaler s, the expression 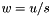 implies
implies 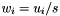 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator/ | ( | const T & | s, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Division operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices v, w, and scaler s, the expression 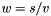 implies
implies 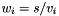 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > operator/ | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | u, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | v | |||
| ) | [related] |
Division operator, with conventional meaning, applied element-by-element. For matrices u, v, and w, the expression 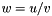 implies
implies 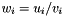 . The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value
. The arrays must conform, that is, have the same dimensions, or an exception with value RWMATH_NMATCH occurs.
| RWMathArray< T > pow | ( | T | x, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | y | |||
| ) | [related] |
| RWMathArray< T > pow | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x, | |
| T | y | |||
| ) | [related] |
| RWMathArray< T > pow | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x, | |
| const RWMathArray< T > & | y | |||
| ) | [related] |
The function pow() takes two arguments: pow( x, y ).
Returns z such that:
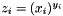
If the number of elements in x does not match the number of elements in y, an exception with value RWMATH_MNMATCH will occur.
| RWMathArray< double > real | ( | const RWMathArray< DComplex > & | ) | [friend] |
Takes a complex argument x and returns real y containing the real part 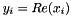 . With most versions of complex, the results can be used as an l-value:
. With most versions of complex, the results can be used as an l-value:
RWMathArray<DComplex> v(5,5,5,0); // (0, 0), (0, 0), ... real(v) = 1.0; // (1, 0), (1, 0), ...
| RWMathArray< T > sin | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | V | ) | [related] |
The function sin() takes x as an argument and returns y such that 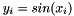 . The xi are in radians. For complex classes, the complex sine is returned.
. The xi are in radians. For complex classes, the complex sine is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > sinh | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | V | ) | [related] |
The function sinh() takes x as an argument and returns y such that 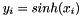 . For complex classes, the complex hyperbolic sine is returned.
. For complex classes, the complex hyperbolic sine is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > sqrt | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | V | ) | [related] |
The square root function. Takes x as an argument and returns y such that 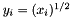 . For complex classes, the principal value of the complex square root is returned.
. For complex classes, the principal value of the complex square root is returned.
| RWMathArray< T > tan | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
The function tan() takes argument x> and returns y such that 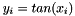 .
.
| RWMathArray< T > tanh | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | x | ) | [related] |
The function tanh() takes argument x and returns y such that 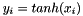 .
.
| RWMathArray< SChar > toChar | ( | const RWMathArray< int > & | v | ) | [related] |
Converts an RWMathArray<int> instance into a corresponding RWMathArray<signed char> instance. Note that this is a narrowing operation; high order bits are removed.
| RWMathArray< float > toFloat | ( | const RWMathArray< double > & | v | ) | [related] |
Converts an RWMathArray<double> instance into a corresponding RWMathArray<float> instance. Note that this is a narrowing operation; high order bits are removed.
| RWGenMat< T > toGenMat | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Converts a 2-dimensional array into a corresponding general matrix class. The array must actually have 2 dimensions or a runtime error occurs. The newly constructed matrix is a new view of the same data as the array; a copy of the data is not made.
| RWMathArray< int > toInt | ( | const RWMathArray< float > & | v | ) | [related] |
Converts an RWMathArray<float> instance into a corresponding RWMathArray<int> instance. Note that truncation occurs.
| RWMathArray< int > toInt | ( | const RWMathArray< double > & | v | ) | [related] |
Converts an RWMathArray<double> instance into a corresponding RWMathArray<int> instance. Note that truncation occurs.
| T toScalar | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Converts a 0-dimensional array into a scalar. The array must actually have 0 dimensions or a runtime error occurs.
| RWMathVec< T > toVec | ( | const RWMathArray< T > & | ) | [related] |
Converts a 1-dimensional array into a corresponding RWMathVec. The array must actually have 1 dimension or a runtime error occurs. The newly constructed vector is a new view of the same data as the array; a copy of the data is not made.
© Copyright Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Rogue Wave and SourcePro are registered trademarks of Rogue Wave Software, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Contact Rogue Wave about documentation or support issues.