
This tutorial will walk you through the steps required to add XML serialization support to an existing MFC Document-View application. (A starter application XMLTutorial is available by request from support@roguewave.com.) All tutorial steps will be based on adding to and changing the code in the XMLSerTut_Base application. You can follow along and make the changes to the code as you go, or refer to the completed application provided in the same directory.
XMLSerTut_Base was generated using the MFC application wizard. It is a very simple drawing program. The user can select shapes from the toolbar and drop them onto the view window

CXShape—The base class for the drawing shapes. This class contains an STL vector of POINT structures.
CXTriangle, CXCircle, and CXRectangle— CXShape-derived classes used to render their respective shapes.
CXDiagram— Custom class that contains an array of CXShape objects.
CDesignDoc — The application's CDocument class. The document data consists of a title and a diagram (CXDiagram object).
In our starter application the CDesignDoc, CXDiagram, and CXShape classes are all serializable classes. Each object is responsible for serializing its internal data. For XML serialization, we will be using helper classes called formatters to write each object's data as XML tags. For this to succeed we need to ensure that the internal data is publicly accessible.
For example, the CXShape class member m_vecPoints is protected. To allow us to read the shape's data, we can add two accessor methods to the class.
We can also add similar logic to the CXDiagram object to give us access to the title and array of shape objects.
We do not need to add public accessors to our document class as we will not be using a formatter class for the document. However, the internal data should be either protected or have protected accessors since we will be creating a new class derived from the existing document class. Read more on this in Section 15.5.4, "XML-enabling the document class."
class CXShape : public CObject
{
...
public:
// Added public accessor to determine how many points in the vector
int GetNumPoints() const;
// Added public accessor to fetch each point from the vector (zero-based)
const POINT& GetPoint(int idx) const;
protected:
std::vector<POINT> m_vecPoints;
};
class CXDiagram : public CObject
{
...
public:
// Added public accessors for title and shape object array
CString GetTitle() const;
CTypedPtrArray<CObArray,CXShape*>* GetShapesArray();
protected:
CTypedPtrArray<CObArray,CXShape*> m_arrShapes;
CString m_strTitle;
};
|
To link in the SFL libraries, we need to make some modifications to our project's stdafx.h (precompiled header file).
// SFL-XML // XML framework requires ATL support #include <atlbase.h> CComModule _Module; #include <atlcom.h> // If you want to link statically to the SFL library // remove the following line #define _SFLDLL // The main header for XML serialization support // We can alternately use sflall.h #include <foundation/xmlserialize.h> |
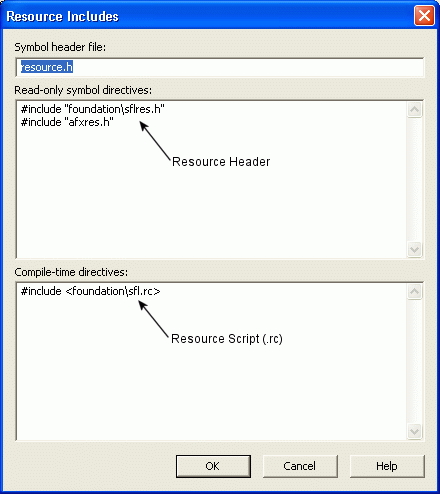
Open up the resource includes dialog via the View | Resource includes... menu option.
Add sflres.h to the read-only symbol directives.
Add sfl.rc at the bottom of the compile-time directives.
The SFL library provides a very handy wrapper class, SECXMLDocAdapter_T, for adding XML serialization to your existing CDocument class. To use this template, simply create a new class that publicly inherits from the template. The template argument is your existing document class.
class CDesignDocXML : public sfl::SECXMLDocAdapter_T<CDesignDoc>
{
...
// Our required override of XMLSerialize
void XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive &ar);
// This method is invoked by the framework to determine
// what the XML tag name will be for our document
virtual void GetElementType(LPTSTR str)
{
_tcscpy(str, _T("DiagramDocument"));
}
};
|
The sfl:: scope declaration is a typedef for the stingray::foundation namespace. You can just as easily add the directive using namespace stingray::foundation; to your header files (or stdafx.h). However, we have chosen to use the sfl:: notation to clearly document where SFL framework classes are being used.
We must provide an implementation of the pure virtual SECXMLDocAdapter_T::XMLSerialize() method. For now, we'll simply provide the boilerplate code.
void CDesignDocXML::XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive &ar)
{
if(ar.IsStoring())
{
// Write out XML
}
else
{
// Read in XML
}
}
|
We provide an override of the GetElementType() method so that the XML framework will know what to call the top-level tag in the XML document. Our resulting XML will look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?> <DiagramDocument> <!-- document data will be child nodes of this top-level node --> </DiagramDocument> |
Now that we have a document class capable of participating in the SFL XML framework, we need to make some small modifications to the application.
In the application object's ::InitInstance() we'll add logic to initialize the OLE libraries and the SFL framework:
BOOL CXMLSerTutApp::InitInstance()
{
// SFL-XML
// Required SFL framework initialization
AfxOleInit();
sfl::SECXMLInitFTRFactory();
...
|
Change the application's CDocTemplate to use the new XML-enabled document class:
CMultiDocTemplate* pDocTemplate;
pDocTemplate = new CMultiDocTemplate(
IDR_XMLSERTYPE,
RUNTIME_CLASS(CDesignDocXML), // new XML-enabled doc class
RUNTIME_CLASS(CChildFrame),
RUNTIME_CLASS(CDesignView));
AddDocTemplate(pDocTemplate);
...
}
|
We'll edit the menu resource to add some entries for loading and saving XML files. This is not absolutely required since the framework will actually parse the file extension when you load or save your document. If the .xml extension is found, the XML framework will call your document's XMLSerialize() override. Otherwise, your base class Serialize(CArchive& ar) method will be invoked.
To handle the menu commands, we make some MESSAGE_MAP entries in our new document class (the one we created from the template and the original document class). You can choose any id value you want for the menu commands, as they aren't predefined in the SFL headers. You do not need to write any message handlers, because they have been provided by the template base class.
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CDesignDocXML, CDocument)
//{{AFX_MSG_MAP(CDesignDocXML)
// Our custom menu commands mapped to the template
// base class handlers
ON_COMMAND(ID_FILE_OPENXML, OnSECFileOpenXML)
ON_COMMAND(ID_FILE_SAVEXML, OnSECFileSaveXML)
ON_COMMAND(ID_FILE_SAVEXMLAS, OnSECFileSaveXMLAs)
//}}AFX_MSG_MAP
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
|
We added public accessors for serializable data to our application classes so that we can create XML formatters to save our objects as XML. A formatter is a simple class that implements the IXMLSerialize interface. The framework contains a base class, CXMLSerializeImp, which can be used as the base class for our formatter classes.
Our formatter has to do three things:
Write class data as XML.
Read class data from XML.
Create a new instance of the class when reading XML.
We'll first concentrate on the first two requirements.
We will create a class hierarchy of formatters that parallels our CXShape class hierarchy. We derive a class from CXMLSerializeImp and provide an override of the XMLSerialize() method.
class CXShapeFMT : public sfl::CXMLSerializeImp
{
public:
// All our CXShape derived classes do their serialization in
// the base class, so we only need one implmentation of
// XMLSerialize, and we can take a base class pointer
CXShapeFMT(CXShape* pShape, LPCTSTR strElementType = _T("Shape"))
: sfl::CXMLSerializeImp(strElementType),m_pShape(pShape)
{
}
virtual ~CXShapeFMT(){}
virtual void XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive& ar);
protected:
// Pointer to the shape we're serializing
CXShape* m_pShape;
};
|
To write out the shape data we need to do the following:
Write out the number of points.
Loop through our POINT vector and write each point's x and y value.
This is the same logic that exists in the standard CXShape::Serialize() method. We use the SECXMLArchive::Read() and ::Write() methods to read and write XML tags. Our first call is to read or write the point count, which will be read from and written to the <PointCount> XML tag. This is the first method parameter.
To ensure that our points can be read back into the object in the correct order, we separate each point as a unique XML child element. Here we have used the format PTxxxxxx to name the XML tags, so that the first point is <PT000001>. Each PTxxxxxx will have two child elements, <XValue> and <YValue>. Even though an STL collection is zero-based, we're using a 1-based naming convention for demonstration purposes.
void CXShapeFMT::XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive &ar)
{
// Shared XML serialization routine for all CXShape classes
int nPointCount = 0;
CString strPointTag;
if (ar.IsLoading()) // Read from XML
{
// Read in the point count
ar.Read(_T("PointCount"),nPointCount);
// Read in each point from the XML document
for(int idx = 0; idx < nPointCount; idx++)
{
// Format the string to create our unique PTxxxxxx tag name
strPointTag.Format(_T("%s%06d"),_T("PT"),(idx+1));
// Open the point tag and read its X and Y values
ar.OpenElement(strPointTag);
POINT ptTemp;
//Add the point to the shape object's vector if successful read
if ((ar.Read(_T("XValue"),ptTemp.x)) && (ar.Read(_T("YValue"),ptTemp.y)))
m_pShape->AddPoint(ptTemp);
// Close the tag
ar.CloseElement(strPointTag);
}
}
else // Write to XML
{
// Write out the point count to the <PointCount> tag
nPointCount = m_pShape->GetNumPoints();
ar.Write(_T("PointCount"),nPointCount);
// Write out each point in the vector
for(int idx = 0; idx < nPointCount; idx++)
{
// Format the string to create our unique tag name
strPointTag.Format(_T("%s%06d"),_T("PT"),(idx+1));
// Open/Create the tag
ar.OpenElement(strPointTag);
// Write the X and Y values
const POINT& ptTemp = m_pShape->GetPoint(idx);
ar.Write(_T("XValue"),ptTemp.x);
ar.Write(_T("YValue"),ptTemp.y);
// Close the tag
ar.CloseElement(strPointTag);
}
}
}
|
We've met our first two requirements for reading and writing our shape class data as XML. So how do we satisfy the third? How can we create an instance of our object from simple XML text?
The SFL framework uses a set of macros that are similar to the MFC FOUNDATION_DECLARE_SERIAL / IMPLEMENT_SERIAL macros. These SFL macros define a lookup map that determines what XML tag corresponds to your domain object classes.
To make our concrete shape classes creatable from XML, we derive three new classes that inherit from the CXShapeFMT class we just created. We're only showing one class, but the procedure is the same for all three.
Our concrete formatter class is doing two things:
Mapping a specific formatter to a specific class.
Describing what the class XML tag will be (via the constructor).
class CXCircleFMT : public CXShapeFMT
{
// Add our class to the XML serialization map
BEGIN_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP(CXCircleFMT)
// First parameter is our domain class,
// second is this formatter class
XMLFORMATTERMAP_ADDENTRY(CXCircle, CXCircleFMT)
END_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP()
public:
// The second parameter to the constructor determines what
// the name of the XML tag will be when writing this object.
CXCircleFMT(CXCircle* pShape, LPCTSTR strElementType = _T("Circle"))
: CXShapeFMT((CXShape*)pShape, strElementType)
{
}
virtual ~CXCircleFMT() {}
};
|
In our implementation (.cpp) file, we use another SFL macro to create an instance of the XML initilization information. The macros we put in the class header declare a static nested class, and we initialize this static instance.
// Everywhere we have declared a BEGIN_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP in a // formatter class requires a matching DEFINE_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP DEFINE_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP(CXCircleFMT) |
The final class for which we need a formatter is our CXDiagram class. The process of declaring the class and initializing the lookup map is the same as it is for the shape classes.
class CXDiagramFMT : public sfl::CXMLSerializeImp
{
// MACROS for initializing the XML formatter map
BEGIN_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP(CXDiagramFMT)
XMLFORMATTERMAP_ADDENTRY(CXDiagram, CXDiagramFMT)
END_SEC_XMLFORMATTERMAP()
public:
CXDiagramFMT(CXDiagram* pDiagram, LPCTSTR strElementType = _T("Diagram"))
: sfl::CXMLSerializeImp(strElementType), m_pDiagram(pDiagram)
{
}
virtual ~CXDiagramFMT(){}
virtual void XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive& ar);
protected:
// Pointer to the diagram we are serializing.
CXDiagram* m_pDiagram;
};
|
Our diagram class needs to write out its title and list of shape objects. In the standard MFC serialization we can write the list of objects with one line of code since we are using a CTypedPtrArray, which provides a Serialize() method.
The SFL framework provides a set of prebuilt formatter classes that can accomplish the same one-line serialization for MFC collection classes. This makes our implementation of XMLSerialize() quite simple.
Here we will use the SFL-provided CTypedPtrArrayFTR formatter class. This is a template class. The two template parameters are the same as the template parameters for the CTypedPtrArray declared in the CXDiagram class.
When we call the SECXMLArchive::Read() method, we pass NULL as the first argument. For the second parameter, we create an instance of the formatter inline. The first parameter to the constructor is a pointer to the diagram's array. The second parameter determines the name of the XML tag representing the collection of objects.
The resulting XML will have this structure:
<Title>Untitled</Title>
<Shapes>
<!-- all the shape nodes here -->
</Shapes>
void CXDiagramFMT::XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive &ar)
{
// We will serialize our title and then the list of child objects
CString strTitle;
CTypedPtrArray<CObArray,CXShape*>* pShapes =
m_pDiagram->GetShapesArray();
if (ar.IsLoading()) // Reading in from XML
{
ar.Read(_T("Title"),strTitle);
m_pDiagram->SetTitle(strTitle);
// Use the SFL- provided formatter to read the collection
ar.Read(NULL,sfl::CTypedPtrArrayFTR<CObArray,
CXShape*>(pShapes,_T("Shapes")));
}
else // Storing to XML
{
strTitle = m_pDiagram->GetTitle();
ar.Write(_T("Title"),strTitle);
// Use the SFL- provided formatter to write the collection
ar.Write(NULL,sfl::CTypedPtrArrayFTR<CObArray,
CXShape*>(pShapes,_T("Shapes")));
}
}
|
Now that we have all our formatter classes written, the only item left is to add serialization code to our new document class.
void CDesignDocXML::XMLSerialize(sfl::SECXMLArchive &ar)
{
// Use our diagram formatter object to handle the XML
// serialization. This parrallels the logic in the standard
// DocView serialization
if(ar.IsStoring())
{
// Write out XML
ar.Write(NULL,CXDiagramFMT(&m_Diagram));
}
else
{
// Read in XML
ar.Read(NULL,CXDiagramFMT(&m_Diagram));
}
}
|
Our results: We can now run our application, create a new drawing, and save it as XML. If we've done everything correctly, our XML will look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<DiagramDocument>
<Diagram>
<Title>Untitled</Title>
<Shapes>
<Size>1</Size>
<Element0>
<Type>Circle</Type>
<Circle>
<PointCount>2</PointCount>
<PT000001>
<XValue>4</XValue>
<YValue>2</YValue>
</PT000001>
<PT000002>
<XValue>104</XValue>
<YValue>102</YValue>
</PT000002>
</Circle>
</Element0>
</Shapes>
</Diagram>
</DiagramDocument>
|
Copyright © Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Rogue Wave name and logo, and Stingray, are registered trademarks of Rogue Wave Software. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Provide feedback to Rogue Wave about its documentation.